Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients – Vancomycin & Midecamycin
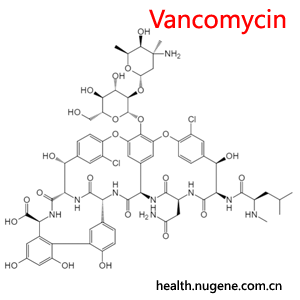
Vancomycin
Vancomycin & Midecamycin – Vancomycin & Midecamycin – Vancomycin is an important antibiotic and is described in detail below:
I. Basic information
Drug type: Glycopeptide antibiotic.
Eli Lilly and Company discovered vancomycin from soil samples collected in Borneo State, Indonesia, where they identified a novel actinomycete, Streptomyces orientalis, that produced this potent antibacterial compound. Researchers found that the active ingredient (initially designated Compound 05865) exhibited remarkable bactericidal properties, demonstrating effectiveness against nearly all staphylococcal strains while showing minimal tendency to induce bacterial resistance. The pharmaceutical industry adopted the name “vancomycin” for this breakthrough antibiotic, which entered clinical use in 1958 after rigorous evaluation.
II. Functions and Indications
Clinicians primarily prescribe vancomycin to combat serious infections when Gram-positive bacteria develop resistance to other antibiotics., such as:
Infections caused by pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci.
Endocarditis, sepsis, pseudomembranous enteritis, etc.
Pneumonia, meningitis, bone and joint infections, osteomyelitis, lung abscess, colitis, etc.
Clinicians sometimes consider vancomycin for preventing infections during implantation of medical devices like cardiac catheters and intravenous catheters.
Third, the mechanism of action
Vancomycin has a triple bactericidal mechanism:
Inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell wall: vancomycin directly combines with D-alanyl-D-alanine at the end of pentapeptide side chain of peptidoglycan precursor of cell wall, preventing the transpeptide action of peptidoglycan polymerase, interfering with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan precursor of bacterial cell wall, so that the cell wall can not form a three-dimensional spatial structure.
Alters the permeability of the bacterial cell membrane.
Blocking the synthesis of RNA in the bacterial cytoplasm.
These mechanisms work together to cause bacterial cell wall defects, water from the external environment continuously seeped into the hypertonic bacterial body, so that the bacterial expansion and deformation death.
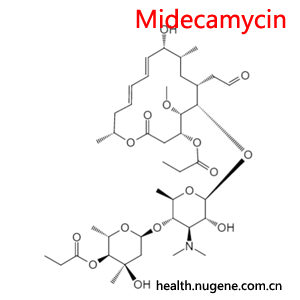
Midecamycin
Madecassicin is a 16-member macrolide antibiotic, which is described in more detail below:
I. Basic Information
Chinese name: Medithromycin
中文同名词: 美地霉素、米地加霉素、米地霉素、麦地霉素、麦白霉素
English name: Midecamycin
Alias: Aboren, Macro-Dil, Midecacine, Medemycin
CAS No.: 35457-80-8
Molecular Formula: C41H67NO15
Molecular weight: 813.96800
Physical and Chemical Properties: Density 1.21g/cm2, Boiling Point 874ºC at 760mmHg, Flash Point 482.4ºC, Refractive Index 1.536, Storage Condition 2~8ºC.
Source and Extraction
Madecassicin was cultured and extracted from Streptomyces sanguinis isolated from soil in Onomichi, Hiroshima, Japan.

